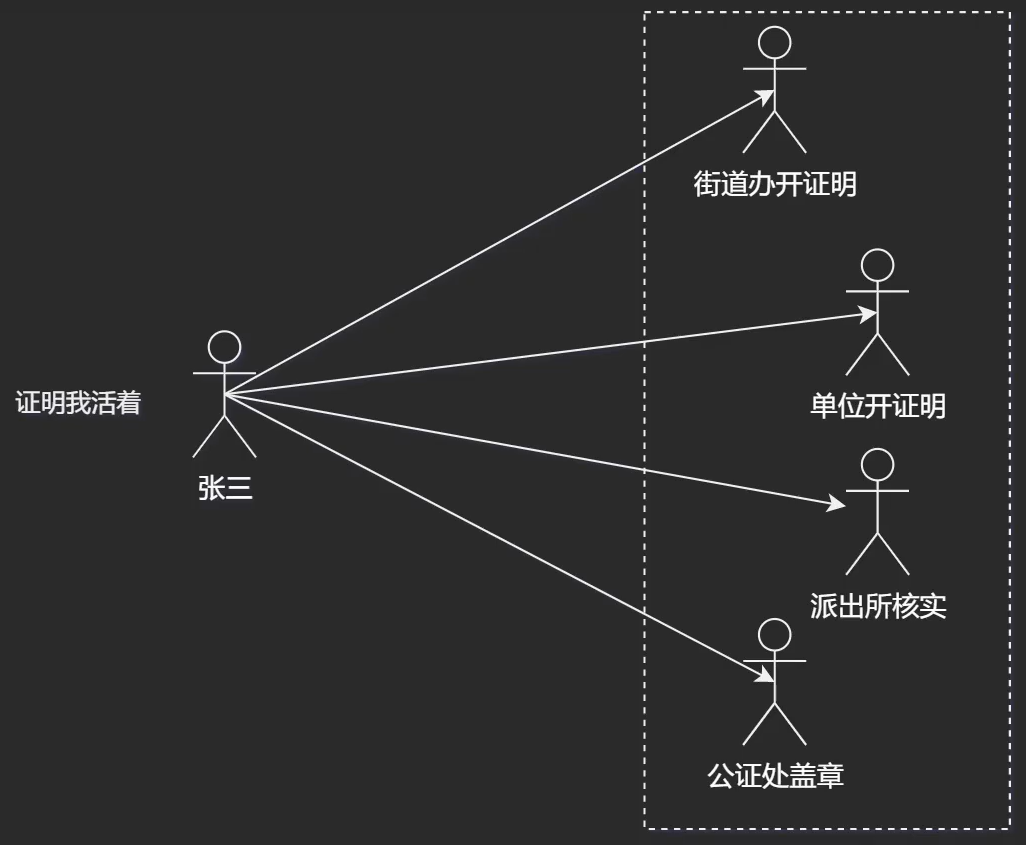
要求一个子系统的外部与其内部的通信必须通过一个统一的对象进行。外观模式提供一个高层次的接口,使得子系统更易使用。
介绍
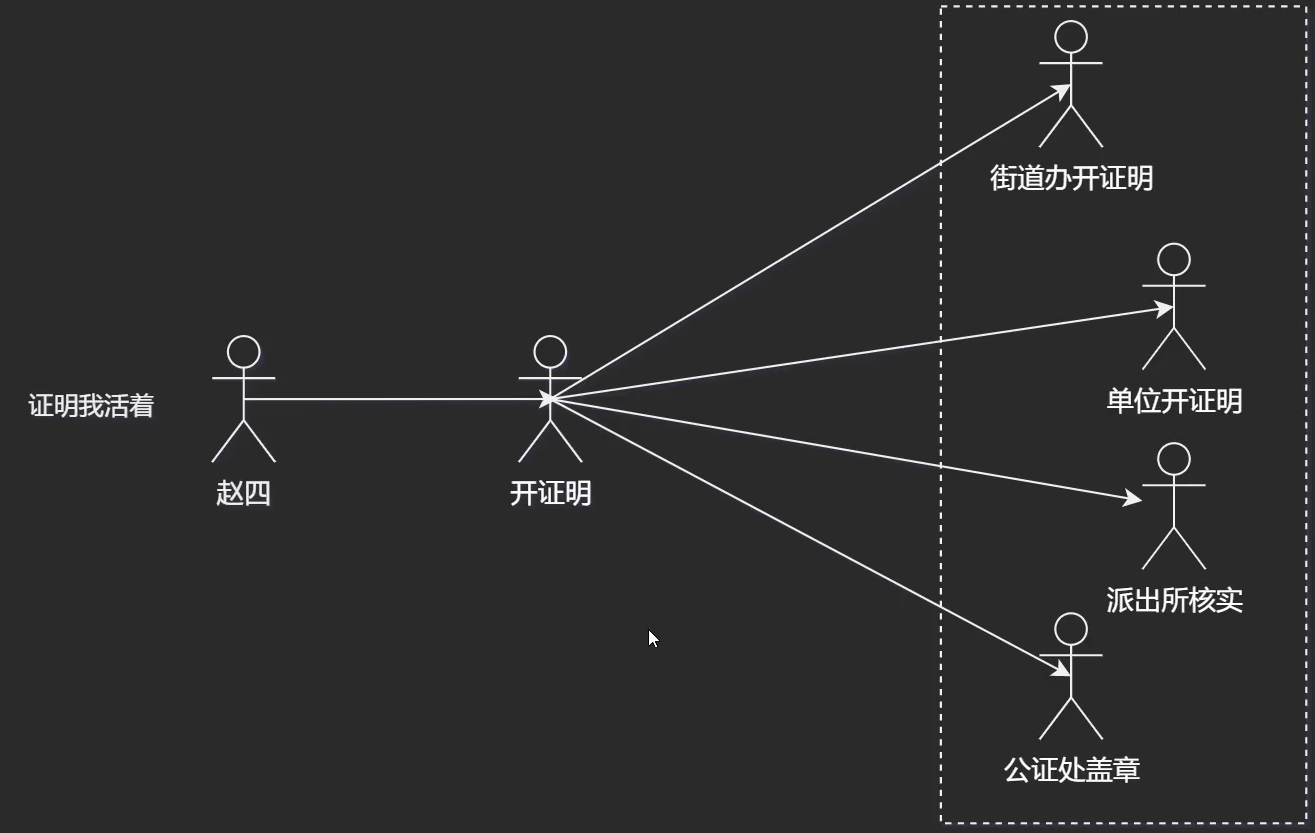
外观模式(Facade Pattern)隐藏系统的复杂性,并向客户端提供了一个客户端可以访问系统的接口。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它向现有的系统添加一个接口,来隐藏系统的复杂性。
这种模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类提供了客户端请求的简化方法和对现有系统类方法的委托调用。
传统模式
外观模式
优缺点及注意
优点
- 为复杂的模块或子系统提供外界访问的模块。
- 子系统相对独立。
- 预防低水平人员带来的风险。
缺点
- 不符合开闭原则。所谓的开闭原则是软件工程里面一个最基本的原则:对扩展开放,对修改关闭。换句话说,你的系统可以提供新的功能模块而不必进行修改。
注意事项
在层次化结构中,可以使用外观模式定义系统中每一层的入口。
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| package com.marlowe;
public class FacadePattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Facade facade = new Facade();
System.out.println(facade.prove());
}
}
class SubFlow1 {
boolean isTrue() {
return true;
}
}
class SubFlow2 {
boolean isOk() {
return true;
}
}
class SubFlow3 {
boolean isGoodMan() {
return true;
}
}
class Facade {
SubFlow1 subFlow1 = new SubFlow1();
SubFlow2 subFlow2 = new SubFlow2();
SubFlow3 subFlow3 = new SubFlow3();
boolean prove() {
return subFlow1.isTrue() && subFlow2.isOk() && subFlow3.isGoodMan();
}
}
|










